About Company
Automation technology that drives the future
Starts with EAST
- Automotive
- Electronics & Semiconductors
- Secondary Batteries
- Food & Beverage · Pharmaceuticals
- Distribution
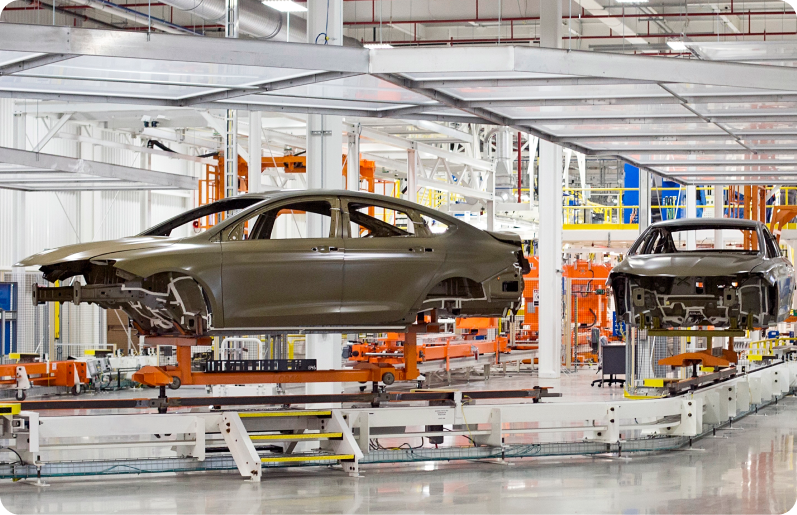

Increasingly sophisticated quality demands, rapidly evolving component structures, and a shortage of skilled labor are emerging as major challenges across the automotive industry.
In particular, in environments that require both precision and speed in production processes, traditional manual inspection and assembly methods struggle to meet the dual goals of quality assurance and production efficiency.
In the midst of these changes, the adoption of automation-based precision inspection and manufacturing systems is no longer optional—it is essential.
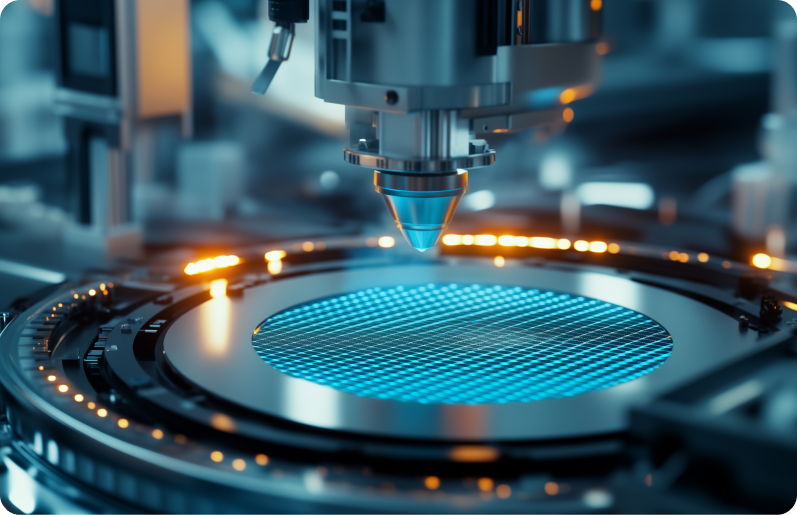

Rapid technological advancements, global supply chain restructuring, ongoing labor shortages, and micro-level quality requirements are emerging as new challenges across the electrical and semiconductor industries.
In particular, in this sector where ultra-fine processes and high-precision components are central, even minor defects can impact overall product yield. As a result, high-speed, high-precision inspection and production automation has become essential.
Driven by the growth of the electric vehicle market, expanding demand for energy storage systems (ESS), and accelerating global carbon neutrality policies,
the secondary battery industry is emerging as one of the most strategically important sectors worldwide.
However, challenges such as high energy density requirements, intensifying cost competition, quality issues, and process safety concerns are creating a pressing need to ensure both production efficiency and quality reliability.
As a result, the implementation of high-precision, high-speed inspection and automation systems has become a core requirement in secondary battery manufacturing sites.
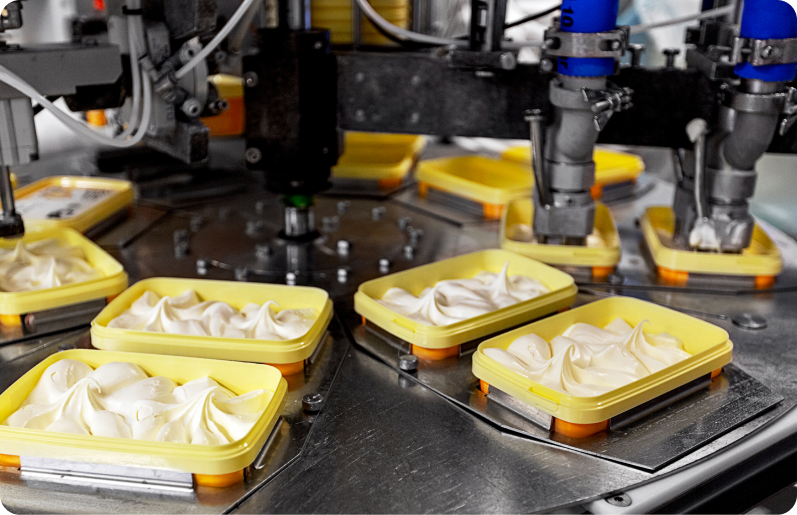

The food and pharmaceutical industries, which are directly linked to consumer safety, are governed by strict standards of hygiene, precision, and stability.
Recently, factors such as population aging, rising demand for health supplements, new drug development, and automation-based GMP compliance have rapidly expanded. Given that even minor process errors can affect overall product quality,
the implementation of precise and hygienic automation systems is emerging as a key driver of competitiveness in the industry.
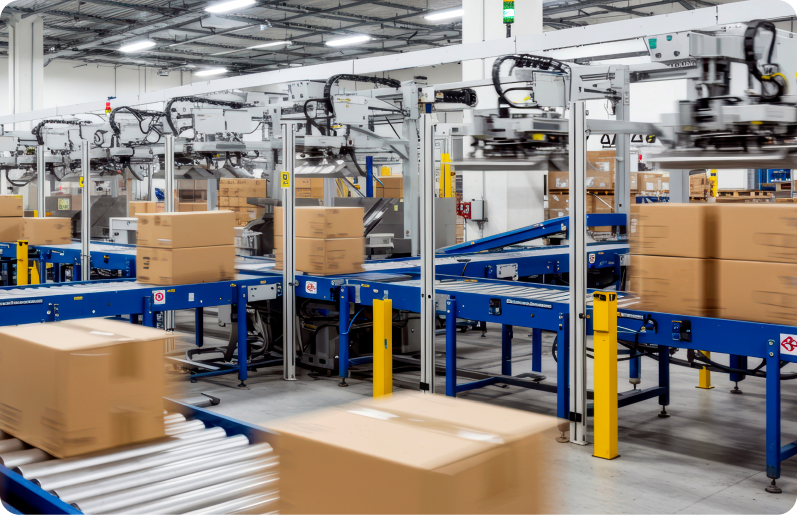

With the expansion of e-commerce, the increase in small-volume, multi-item deliveries, and intensifying competition for same-day and next-day shipping,
the logistics and distribution industry is facing an unprecedented demand for structural innovation centered on speed, accuracy, and efficiency.
In particular, labor-dependent work environments and repetitive manual processes are major contributors to rising costs and increased error rates,
making logistics process innovation through automation systems an essential challenge.
Camera vision-based automation solutions detect even the tiniest defects that are easily missed by the human eye in real time, significantly reducing defect rates and improving quality reliability.
Automated systems can operate reliably 24/7, maintaining consistent quality and speed without relying on worker proficiency, thereby greatly enhancing delivery responsiveness and overall productivity.
Automation of processes helps reduce unnecessary material waste and energy loss, contributing to the creation of a sustainable manufacturing environment and the achievement of ESG goals.
Sensor- and software-based predictive maintenance systems detect equipment anomalies in advance and prevent breakdowns, minimizing downtime and reducing maintenance costs.
Automation systems that detect microscopic defects in real time significantly reduce defect rates within the process
and help maintain stable yield levels.
By combining AI-based analysis with robotic automation, both the speed and precision of repetitive tasks can be improved,
eliminating process bottlenecks and optimizing overall production flow.
This is especially effective in semiconductor back-end processes where high-speed mass production is critical.
Reducing reliance on skilled workers enables consistent quality without fatigue or judgment variability.
This is a key factor in ensuring reliability and reproducibility in the electrical and electronics industries,
where multi-variety, small-volume production is common.
Automating processes helps reduce unnecessary material waste and energy loss,
contributing to the creation of a sustainable manufacturing environment and the achievement of ESG goals.
Since secondary batteries contain components directly related to safety, even microscopic defects can pose serious risks.
Automated vision inspection systems detect subtle anomalies in electrodes, tabs, pouches, and welds in real time,
preventing quality issues in advance and supporting stable product output.
AI-powered automation equipment accelerates repetitive tasks and minimizes human intervention,
reducing defect rates and improving overall yield. Especially in processes like electrode alignment, stacking, and welding,
it maximizes productivity by balancing precision and speed.
Battery manufacturing involves inherent risks such as fire and explosion, making data-driven monitoring
and predictive systems essential. Automation equipment detects abnormal conditions early and diagnoses equipment status
in real time, minimizing process-related risks.
By quickly adapting to changing production conditions and improving energy efficiency, sustainability is enhanced.
This enables the achievement of ESG goals and the creation of a flexible manufacturing environment.
In food and pharmaceutical production, even minor errors such as foreign substance contamination, dosage deviation, or sealing defects
can lead to critical issues. Automation systems are essential for maintaining consistency and precision in repetitive tasks within sterile environments.
Equipment technologies that support micro-level transplantation, filling, and cutting processes are especially suitable for medical and bio-automation
applications.
The food and pharmaceutical industries demand both scale and speed. Automation solutions
enable consistent handling of high-speed packaging, filling, labeling, and inspection processes, reducing defect rates and
facilitating traceability throughout the production history.
Contamination, foreign substance mixing, and operational deviations caused by unskilled workers or repetitive tasks
pose significant risks in food and pharmaceutical production. Automation minimizes human intervention and supports compliance with
regulations such as GMP and HACCP, ensuring consistent quality and hygiene standards.
By improving energy efficiency and reducing resource consumption, automation helps minimize waste generation
while meeting hygiene standards and environmental regulations, contributing to a sustainable production environment.
AI-powered automation systems recognize product specifications, barcodes, and location data
to perform automatic sorting and transport, enabling fast and accurate operations without human intervention
and significantly improving overall operational efficiency.
Automation systems accurately handle repetitive tasks such as packaging, sorting, loading, and tracking,
reducing worker fatigue and human error, and creating a highly reliable logistics environment.
Automation systems integrated with sensors enable real-time monitoring and management of logistics flow and inventory status,
helping reduce unnecessary stock, prevent delivery delays, and enhance operational stability.
Automation systems optimize logistics routes and reduce energy consumption, minimizing material waste and packaging usage
to support the creation of eco-friendly logistics environments.
Additionally, unmanned operations help reduce carbon emissions and enable the development of a sustainable distribution ecosystem.
Automotive Industry Technology
Electrical & Semiconductor Industry Technology
Secondary Battery Industry Technology
Food & Pharmaceutical Industry Technology
Distribution Industry Technology
- Automated Production Line Equipment
- Inspection & Assembly Line Equipment
- Integrated Management Software
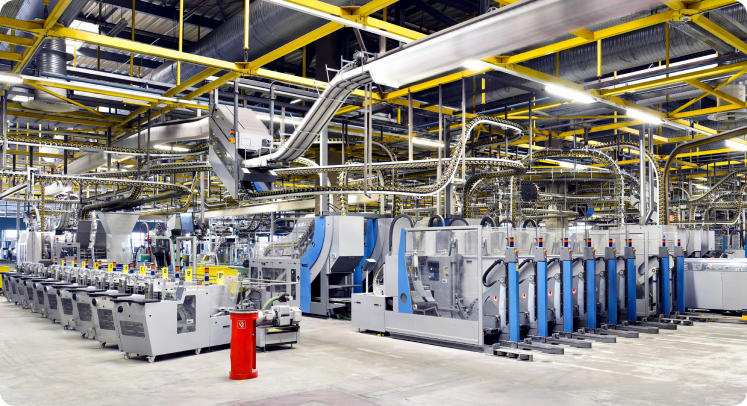

We design and build customized automated production lines tailored to precision assembly processes and diverse product categories. Advanced automation is implemented across all stages of production—including assembly, welding, and machining—to maximize quality consistency and production efficiency.
-

Design and manufacture dedicated automation booths that reflect product characteristics and production conditions, enhancing operational stability and production efficiency.
-

Configure welding lines optimized for high-temperature and high-risk environments to ensure uniform welding quality and operator safety.
-

Maximize space utilization through CAD-based precision design and minimize potential errors with pre-production simulation.
-

Visualize the entire process flow and automation elements through initial concept designs for clear and comprehensive planning.











